Have you ever wondered how your cute little dog sees the world? Like us humans, dogs sense the world around them, but their vision, smell and hearing are completely different from ours. Dogs see colors in a limited way, but their night vision and ability to detect motion are amazing.
Also, they experience the world through smell, which is an invisible means of communication for them. In this blog we will learn how the sensory world of dogs affects their behavior and their relationship with us.
What is the difference between the eyes of dogs and humans
Dogs experience the world in a unique way, especially when it comes to vision. While humans see vibrant colors and fine details, dogs perceive colors more mutedly—mainly in shades of blue and yellow.
Their eyes are also more sensitive to motion, helping them detect even slight movements, a trait inherited from their hunting ancestors. However, dogs don’t see as sharply as humans, and their night vision is far better thanks to a special reflective layer in their eyes.
Understanding these differences helps us appreciate how our furry companions navigate the world—not worse or better, just differently
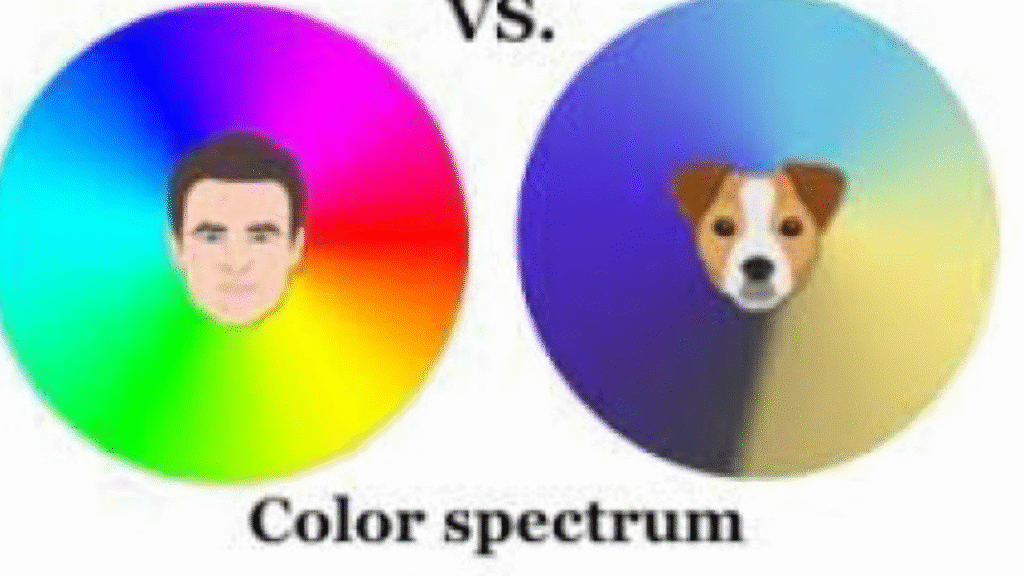
Can dogs see colors or not
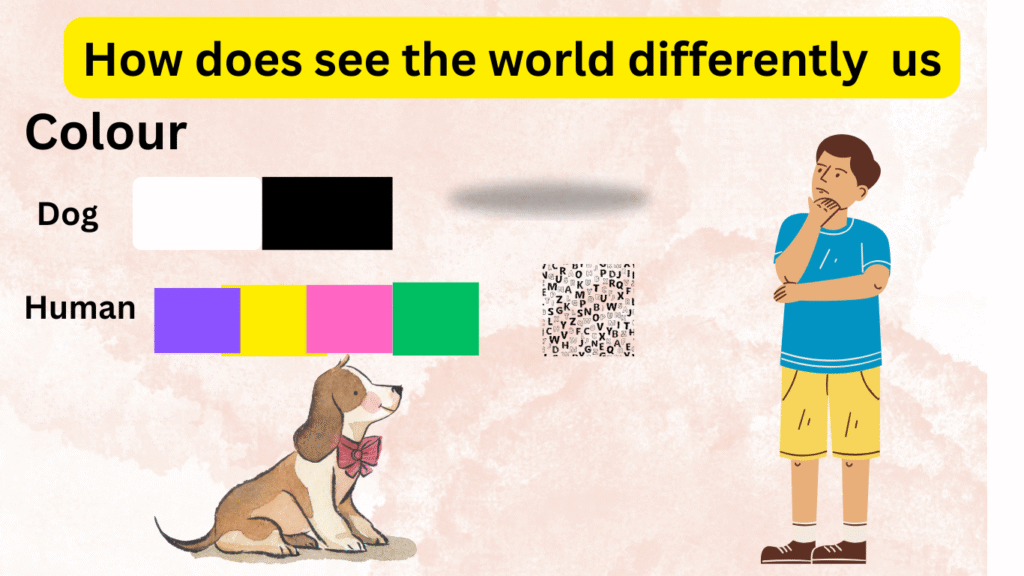
Many people are curious about whether dogs can see colors or if their world is only black and white. In reality, dogs do perceive colors, but not as vividly as humans. Unlike humans, who have three types of color receptors (red, green, and blue), dogs have only two—blue and yellow.

As a result, they can differentiate between blue and yellow hues but have difficulty recognizing red and green, which often appear as muted tones like gray or brown. So, even though dogs don’t see the full spectrum of colors that we do, their vision isn’t limited to black and white—it’s just less vibrant.
What things can dogs see better
Dogs experience the world in a way that’s quite different from humans. While we rely heavily on our color vision, dogs see fewer colors but are far better at detecting movement and seeing in low light. That’s why they’re excellent at spotting small animals or noticing something unusual in the dark.
How dogs see the world differently from us lies in their ability to use other senses too—like smell and hearing—which are far more advanced than ours. What things can dogs see better includes motion, contrast, and night vision, helping them navigate and protect their surroundings effectively.
Dogs’ ability to see in the dark
Dogs have a special ability to see better in the dark than humans. This is because their eyes have more rod cells, which help detect light and movement in low-light conditions. They also have a layer behind the retina called the tapetum lucidum, which reflects light and makes their night vision sharper.
That’s why dogs can easily move around at night or in dim rooms without bumping into things. While they may not see sharp details, they can sense shapes and motion clearly. This natural night vision comes from their wild ancestors, who needed it to hunt in the dark.
What is the world like as seen by dogs
Dogs experience the world in ways we can only imagine. While humans rely heavily on vision, dogs perceive their surroundings through a blend of sharp senses—smell, hearing, and even subtle body language.
Their eyes detect motion better than fine details, and their color vision is limited compared to ours, seeing shades of blue and yellow rather than a full rainbow. But what they lack in visual clarity, they make up for with an incredible sense of smell, picking up scents we’d never notice. For them, every walk is a rich tapestry of smells, sounds, and instincts guiding their way.
Scientific analysis of dogs’ vision
Dogs see the world in a way that’s quite different from humans. While we enjoy a wide range of colors, dogs view the world mostly in shades of blue and yellow. This is because their eyes have fewer color-detecting cells, called cones. However, what they lack in color vision, they make up for with better motion detection and night vision.
Scientifically, dogs have more rod cells in their eyes, which help them see well in low light. Their vision is specially adapted for hunting and sensing movement, making them excellent companions with a unique way of understanding their surroundings.
Do dogs see us the way we see them
Dogs experience the world in ways that are very different from humans. While we rely heavily on our sharp vision and color perception, dogs see fewer colors (mostly blues and yellows) but excel in detecting motion and seeing in low light. Their world is more about smells and sounds—every walk is an exciting scent adventure!
But do they see us the same way we see them? Probably not. Dogs interpret our body language, tone, and energy more than our appearance. To them, we’re not just owners—we’re family, protectors, and lifelong companions, seen through a unique, loving lens.
Limitations and strengths of dogs’ vision
Dogs see the world in a way that’s quite different from humans. While they can’t see the full range of colors we do—mainly viewing the world in shades of blue and yellow—their vision has unique strengths. Dogs are far better at seeing in low light, thanks to more rod cells in their eyes.

This helps them navigate well at dawn or dusk. However, their visual sharpness is lower than ours, meaning they may not notice fine details. Despite this, dogs are excellent at detecting motion, which plays a key role in hunting and sensing danger around them.
Dogs’ side vision vs. our vision
Dogs and humans experience the world in very different ways, especially when it comes to vision. While humans have forward-facing eyes that provide better depth perception, dogs have eyes placed more on the sides of their heads. This gives them a wider field of view, allowing them to spot movement from nearly 240 degrees around them.
However, this comes at the cost of less depth perception and clarity in close-up vision. Unlike humans, dogs rely more on motion detection than detail. Their unique vision helps them stay alert, hunt, and respond quickly to their surroundings in the wild.
How to understand the difference between human and dog vision
Understanding the difference between human and dog vision reveals fascinating insights about how dogs experience the world. Humans have three types of cones in their eyes, enabling them to see a wide spectrum of colours, including red, green, and blue.
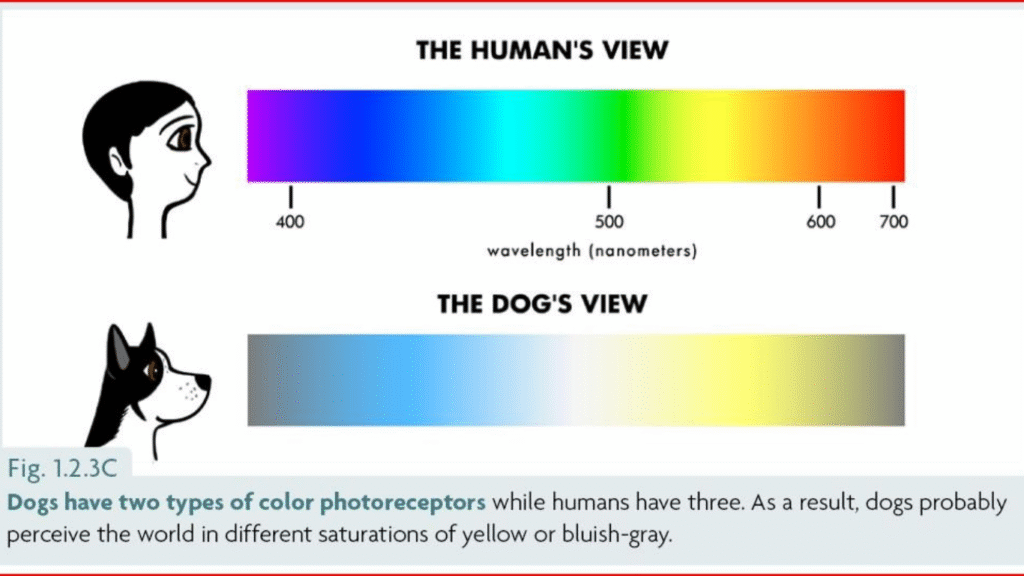
In contrast, dogs have only two types of cones, limiting their colour perception to shades of blue and yellow, similar to red-green colour blindness in humans. Additionally, dogs’ vision is better suited for low light and motion detection due to a higher number of rods in their eyes.
While human vision is sharper and more colorful, dogs excel in night vision and detecting subtle movements.
FAQ
Dogs can’t see in complete darkness, but their vision is much better than humans in low light. Their eyes have more light-sensitive cells and a special layer called the tapetum lucidum that reflects light, helping them see better at dusk or dawn.
However, they still need some light to see—like moonlight or a dim lamp. In total darkness, dogs rely more on their strong sense of smell and hearing to navigate. So, no night-vision superpowers, but they do see better than us in the dark!
A dog’s vision is different from humans. They see fewer colors—mostly blues and yellows, not reds or greens. Their world is less sharp, like a slightly blurry picture.
But they’re great at spotting movement, even in dim light, thanks to better night vision. Dogs also have a wider field of view (around 240 degrees vs. our 180 degrees), helping them detect things around them faster. However, their depth perception isn’t as precise as ours.
A dog’s sense of smell is incredibly powerful—it can detect scents up to 12 miles away in ideal conditions! However, this depends on factors like wind, weather, and the strength of the odor.
For example, tracking dogs can follow a trail days old, while search-and-rescue dogs sniff out people buried under rubble. Their noses are millions of times more sensitive than ours, making them amazing at picking up faint smells we’d never notice!
Dogs enjoy sleeping between your legs because it makes them feel safe, warm, and comforted. Your legs provide a cozy space that reminds them of snuggling with their littermates as puppies.
It also helps them feel protected and close to you, strengthening their bond with you. This behavior is their way of seeking security and affection. However, it’s also a sign of trust—they feel relaxed enough to be in such close proximity and rest peacefully.
Read Other Also
Can dogs travel with you on planes
Best Dog Food for Humans to Eat – Safe & Tasty Options You Won’t Believe
Should I get a dog or cat? Here’s How to Know Which One’s Right for You
What do boxer dogs eat? A complete guide to their nutritional needs

